How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a question many aspiring pilots ask. This guide delves into the intricacies of drone operation, from understanding fundamental regulations and safety protocols to mastering advanced flight techniques and capturing stunning aerial footage. We’ll cover everything from pre-flight checklists and component familiarity to troubleshooting common issues and maintaining your drone for optimal performance.
Whether you’re a complete beginner or looking to refine your skills, this comprehensive resource will equip you with the knowledge and confidence to take to the skies responsibly.
We’ll explore the essential aspects of drone piloting, including legal considerations, technical understanding of your drone’s components, and practical guidance on safe and efficient flight operations. We’ll also delve into advanced techniques such as waypoint navigation and automated flight modes, enabling you to unlock the full potential of your drone for both recreational and professional applications. The goal is to provide a clear, concise, and practical roadmap for anyone eager to learn how to operate a drone.
Drone Regulations and Safety
Operating a drone responsibly requires understanding and adhering to both legal regulations and crucial safety procedures. These guidelines vary significantly across jurisdictions and are vital for ensuring safe and legal drone operation.
Drone Regulations by Region
Drone laws differ considerably depending on your location. For example, in the United States, the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) regulates drone use, requiring registration for certain drone types and limiting flight zones. Similarly, the European Union has established comprehensive drone regulations, emphasizing safety and privacy. Countries like Canada, Australia, and the UK also have their own specific rules and regulations.
It’s crucial to research and comply with the regulations specific to your region before operating any drone.
Drone Safety Procedures
Safety should be the paramount concern during every stage of drone operation. This includes pre-flight checks, adherence to safe flight practices during operation, and post-flight procedures for maintenance and storage.
Pre-Flight Drone Inspection Checklist
A thorough pre-flight inspection is essential for preventing accidents. This checklist should be completed before each flight.
- Battery charge level
- Propeller condition and secure attachment
- GPS signal strength and accuracy
- Camera functionality and settings
- Gimbal stability
- Drone body for any damage
- Controller functionality and battery
- Review of local flight restrictions
Commercial vs. Recreational Drone Use Regulations

The regulations governing commercial and recreational drone use often differ significantly.
| Regulation Category | Commercial Use | Recreational Use | Penalties for Violations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Registration | Usually required, with additional permits and licenses | May be required depending on the drone’s weight and location | Fines, suspension of operating privileges |
| Operating Restrictions | Stricter limitations on flight zones, altitudes, and airspace | More relaxed restrictions, but still subject to airspace limitations | Fines, imprisonment (in severe cases) |
| Insurance | Generally required | Often not required, but recommended | Civil liability for damages |
| Pilot Certification | Often requires a Remote Pilot Certificate | Usually not required | Operating privileges revoked |
Understanding Drone Components and Controls
Familiarizing yourself with your drone’s components and how to operate its controls is essential for safe and effective flight.
Drone Components and Their Functions, How to operate a drone
Drones consist of several key components, each playing a crucial role in flight. These include the frame, motors, propellers, flight controller, battery, GPS module, and camera. The frame provides structural support, motors power the propellers, the flight controller manages flight stability and responsiveness, the battery provides power, the GPS aids navigation, and the camera captures images and videos.
Types of Drone Controllers and Functionalities
Drone controllers vary in design and features. Some are basic, providing only essential flight controls, while others incorporate advanced features like programmable flight modes and real-time telemetry displays. Many modern controllers offer customizable settings to adjust sensitivity and response curves to suit the pilot’s preference.
Drone Sensor Calibration
Calibrating a drone’s sensors, such as the IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit) and barometer, is crucial for accurate and stable flight. The specific calibration procedure varies depending on the drone model, but generally involves powering on the drone, following the manufacturer’s instructions, and allowing the sensors to initialize and calibrate themselves.
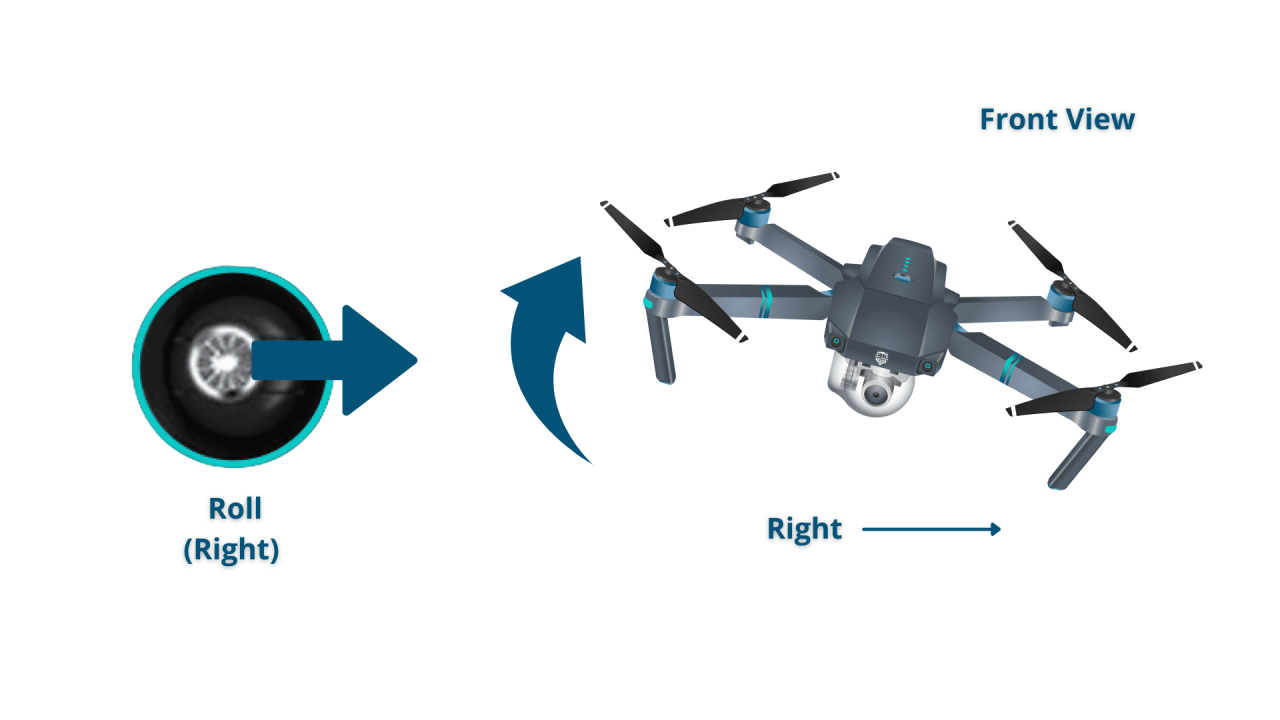
Drone Control Stick Movements
The control sticks on a typical drone controller typically have two pairs of sticks: one pair controls the drone’s yaw and throttle (rotation and vertical movement), while the other pair controls the drone’s roll and pitch (forward/backward and left/right movement). Pushing the left stick forward moves the drone forward, pulling it back moves it backward, pushing it left moves it left, and pushing it right moves it right.
The right stick controls the drone’s rotation and altitude. A slight push on the right stick will cause the drone to rotate slowly. Pushing the stick all the way to the right or left will cause the drone to rotate quickly. Pushing the stick up will cause the drone to ascend, and pushing it down will cause it to descend.
Pre-Flight Preparations and Checklists
Meticulous pre-flight preparation is vital for a successful and safe drone flight. This includes thorough checks of the drone, battery management, and flight path planning.
Pre-Flight Drone Preparation Checklist
This checklist ensures all necessary steps are taken before launching the drone.
- Inspect the drone for any damage
- Charge the drone’s battery to the recommended level
- Check the GPS signal strength and satellite lock
- Verify the camera settings
- Test the controller’s connection to the drone
- Plan the flight path, considering obstacles and weather conditions
- Review any local airspace restrictions
Battery Management and Charging Procedures
Proper battery management is crucial for drone safety and longevity. Always use the manufacturer’s recommended charger and follow the charging instructions carefully. Avoid overcharging or discharging batteries, and store them in a cool, dry place when not in use.
Safe Flight Path Planning
Planning a safe flight path involves identifying potential hazards, such as buildings, trees, power lines, and people. Consider weather conditions, such as wind speed and direction, and ensure the drone remains within the legal and safe operating limits. It is recommended to always fly within visual line of sight (VLOS) unless specifically permitted otherwise.
Essential Pre-Flight Checks for Different Drone Models
| Drone Model | Battery Check | Propeller Check | GPS Signal Check |
|---|---|---|---|
| DJI Mavic 3 | Voltage and cell balance | Secure attachment and no damage | Number of satellites and signal strength |
| Autel EVO II | Battery level indicator and remaining flight time | Tightness and condition of propellers | GPS lock indicator and accuracy |
| Parrot Anafi | Battery level and health | Visual inspection for cracks or damage | GPS signal strength and accuracy |
Basic Drone Flight Operations
Taking off, hovering, and landing a drone smoothly requires practice and understanding of the controls. This section details the steps involved.
Taking Off, Hovering, and Landing
To take off, power on the drone and controller, wait for the GPS signal to lock, and gently push the throttle stick upwards. To hover, maintain a steady throttle position. To land, slowly lower the throttle stick.
Controlling Altitude, Direction, and Speed
Altitude is controlled by the throttle stick, direction by the left directional stick, and speed by the responsiveness of the stick movements. Smooth and controlled inputs are key to precise maneuvering.
Tips for Smooth and Controlled Maneuvers
Practice smooth and deliberate stick movements. Avoid jerky inputs, which can destabilize the drone. Use the drone’s different flight modes (e.g., Beginner, Sport) to adjust responsiveness to your skill level. Pay close attention to wind conditions and adjust your flight accordingly.
Common Mistakes of Beginner Drone Pilots
Common mistakes include jerky stick movements, ignoring wind conditions, and flying too close to obstacles. Learning to fly in open areas and gradually increasing the complexity of maneuvers is advisable.
Advanced Drone Flight Techniques
Once comfortable with basic flight operations, exploring advanced techniques like waypoint navigation and automated flight modes enhances your capabilities.
Waypoint Navigation and Automated Flight Modes
Waypoint navigation allows you to pre-program a flight path, enabling the drone to autonomously follow a series of points. Automated flight modes, such as “Follow Me” or “Point of Interest,” offer additional automated flight capabilities.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires careful planning and adherence to regulations. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, including safety protocols and legal requirements, please refer to this excellent resource on how to operate a drone. This will help ensure safe and responsible drone piloting.
Ultimately, mastering how to operate a drone is about practice and understanding the technology.
Use of GPS and Other Navigation Systems

GPS is crucial for accurate positioning and navigation. Some drones also utilize other sensors, such as IMU and barometer, for enhanced stability and precision.
Comparison of Flight Modes
Different manufacturers offer various flight modes. Understanding the features and limitations of each mode is important for safe and efficient operation. For example, some modes offer more stability at the cost of responsiveness, while others prioritize speed and maneuverability.
Performing a 360-Degree Aerial Shot
To perform a 360-degree aerial shot, position the drone at the desired altitude and location. Engage a circular flight mode (if available), or manually control the drone’s yaw to rotate smoothly in a circle, ensuring consistent altitude and speed. Proper camera settings and steady hand movements are vital for a smooth, cinematic effect.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance is essential for ensuring your drone’s optimal performance and longevity. This includes routine cleaning, inspections, and addressing any malfunctions promptly.
Routine Drone Maintenance Tasks
Routine maintenance includes cleaning the drone body and propellers, checking for loose screws or damaged components, and lubricating moving parts as per the manufacturer’s recommendations. Regularly inspect the battery for any signs of damage or swelling.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Causes
Common malfunctions include GPS signal loss, motor failures, battery issues, and camera malfunctions. Causes can range from software glitches to physical damage.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Problems
Troubleshooting involves systematically checking components, re-calibrating sensors, and checking for software updates. Consulting the drone’s manual and online resources can often provide solutions to common problems.
Regular Drone Maintenance Schedule
| Maintenance Task | Frequency | Tools Required | Steps |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clean drone body and propellers | After each flight | Soft cloth, isopropyl alcohol | Gently wipe down all surfaces, avoiding contact with electronics. |
| Inspect propellers for damage | Before each flight | Visual inspection | Check for cracks, bends, or other damage. Replace damaged propellers. |
| Check battery health | Weekly | Battery analyzer (optional) | Inspect for swelling or damage. Check voltage and cell balance. |
| Check for loose screws or parts | Monthly | Screwdriver | Tighten any loose screws or replace damaged parts. |
Drone Photography and Videography: How To Operate A Drone
Capturing high-quality aerial photos and videos requires understanding camera settings and composition techniques.
Capturing High-Quality Photos and Videos
High-quality aerial media depends on several factors, including appropriate camera settings, stable flight, and good lighting. Experiment with different settings such as ISO, shutter speed, and aperture to achieve the desired image quality. Consider using ND filters to manage light levels and achieve a shallow depth of field.
Camera Settings and Impact on Image Quality
Understanding the relationship between ISO, shutter speed, aperture, and white balance is crucial for achieving optimal image quality. Higher ISO values increase sensitivity to light but can introduce noise. Slower shutter speeds allow for more light but can lead to motion blur. Aperture controls depth of field, affecting the focus and blur of the background. White balance adjusts the color temperature to ensure accurate color representation.
Tips for Composing Compelling Aerial Shots
Consider the rule of thirds, leading lines, and framing to create visually appealing compositions. Experiment with different angles and perspectives to find unique shots. Plan your shots in advance, considering lighting, shadows, and the overall scene.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating these aspects requires practice and a solid understanding of the regulations. For a comprehensive guide covering all these elements, check out this helpful resource on how to operate a drone and ensure safe and effective drone flights. Remember, responsible operation is paramount.
Editing Drone Footage
Editing drone footage involves using video editing software to enhance the footage and create a compelling narrative. This involves trimming clips, adding transitions, adjusting colors, and incorporating music or sound effects. Common steps include importing footage, trimming unwanted sections, color correction, adding transitions, and exporting the final video in a desired format and resolution.
Mastering drone operation requires a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical experience. By understanding drone regulations, familiarizing yourself with your drone’s components, and practicing safe flight techniques, you can unlock the exciting possibilities of aerial exploration and photography. Remember to always prioritize safety, respect local regulations, and continue learning to refine your skills. With dedication and practice, you’ll be confidently navigating the skies and capturing breathtaking perspectives in no time.
This comprehensive guide serves as a foundation for your drone piloting journey; now go out there and explore the world from above!
Answers to Common Questions
What type of drone is best for beginners?
User-friendly drones with GPS stabilization and autonomous flight modes are ideal for beginners. Look for models with intuitive controls and safety features.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s sensors?
Calibrate your drone’s sensors before each flight, or if you notice erratic behavior. Refer to your drone’s manual for specific calibration instructions.
What should I do if my drone loses signal?
Most drones have a “return-to-home” (RTH) function. Activate this if signal is lost. If RTH fails, attempt to manually regain control. If unsuccessful, locate your drone using its last known location.
How long does a drone battery typically last?
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the model, usage, and weather conditions. Check your drone’s specifications for an estimated flight time.
